-
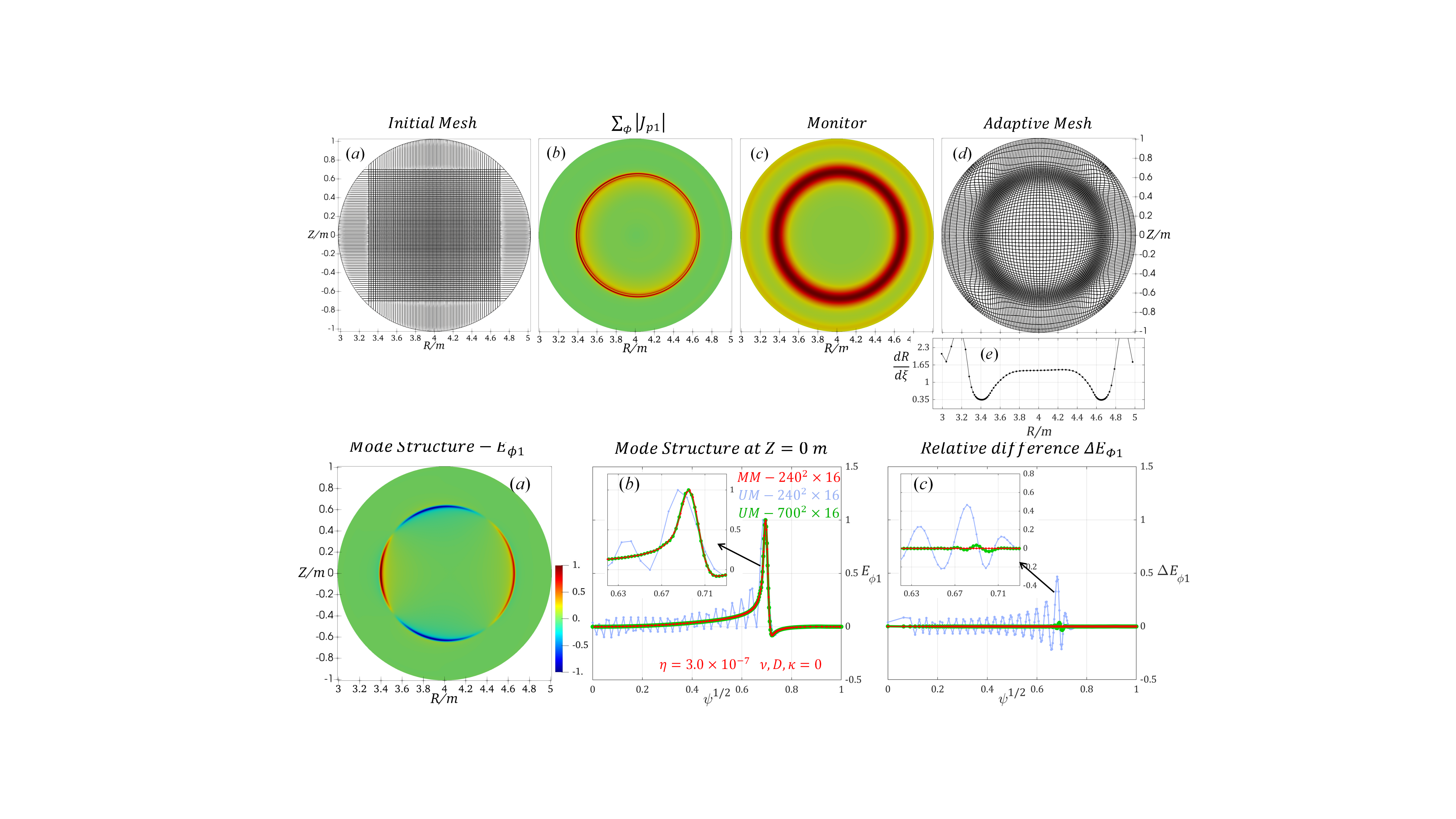 An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations J. Wang a , J.M. Duan b , Z.W. Ma a,* , W. Zhang a a:Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, Chinab:Ecole ´ Polytechnique F´ed´erale de Lausanne, 1015 Lausanne, SwitzerlandAn adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme is developed for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) simulations, based on the CLT code (S. Wang and Z.W. Ma, Phys. Plasmas, 2015). Our numerical scheme is built on the MHD equations in curvilinear coordinates, based on a coordinate transformation from the physical domain to a computational domain. The scheme is constructed on a uniform Cartesian computational mesh that is obtained from a non-uniform adaptive moving mesh in the physical domain through the coordinate transformation. Mesh points in the physical domain in general move and concentrate in the vicinity of solutions with rapid variations by solving an adaptive mesh equation, whilst total number of mesh points remains unchanged. The local resolution can be significantly increased and computational resource is largely reduced. Comparison between results obtained with the original uniform mesh and the new adaptive moving mesh is carried out by simulation of the linear and nonlinear 2/1 tearing mode, linear and nonlinear 1/1 resistive internal kink mode. It is found that the adaptive moving mesh scheme possesses better numerical stability and convergence.
An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations J. Wang a , J.M. Duan b , Z.W. Ma a,* , W. Zhang a a:Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, Chinab:Ecole ´ Polytechnique F´ed´erale de Lausanne, 1015 Lausanne, SwitzerlandAn adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme is developed for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) simulations, based on the CLT code (S. Wang and Z.W. Ma, Phys. Plasmas, 2015). Our numerical scheme is built on the MHD equations in curvilinear coordinates, based on a coordinate transformation from the physical domain to a computational domain. The scheme is constructed on a uniform Cartesian computational mesh that is obtained from a non-uniform adaptive moving mesh in the physical domain through the coordinate transformation. Mesh points in the physical domain in general move and concentrate in the vicinity of solutions with rapid variations by solving an adaptive mesh equation, whilst total number of mesh points remains unchanged. The local resolution can be significantly increased and computational resource is largely reduced. Comparison between results obtained with the original uniform mesh and the new adaptive moving mesh is carried out by simulation of the linear and nonlinear 2/1 tearing mode, linear and nonlinear 1/1 resistive internal kink mode. It is found that the adaptive moving mesh scheme possesses better numerical stability and convergence.
-
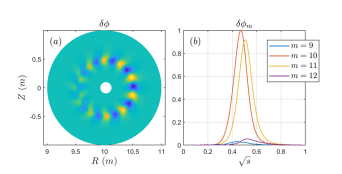 Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfven eigenmodes driven by energetic particles
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfvén eigenmodes driven by energetic particles Z. Y. Liu ; P. Y. Jiang ; S. Y. Liu ; L. L. Zhang ; G. Y. Fu ABSTRACT We have developed a hybrid code GMEC: Gyro-kinetic Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Energetic-particle Code that can numerically simulate energetic particle-driven Alfvén eigenmodes and energetic particle transport in tokamak plasmas. In order to resolve the Alfvén eigenmodes with high toroidal numbers effectively, the field-aligned coordinates and meshes are adopted. The extended MHD equations are solved with the five-point finite difference method and the fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. The gyrokinetic equations are solved by particle-in-cell method for the perturbed energetic particle pressures that are coupled into the MHD equations. Up to now, a simplified version of the hybrid code has been completed with several successful verifications, including linear simulations of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes and reversed shear Alfvén eigenmodes.
Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfven eigenmodes driven by energetic particles
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfvén eigenmodes driven by energetic particles Z. Y. Liu ; P. Y. Jiang ; S. Y. Liu ; L. L. Zhang ; G. Y. Fu ABSTRACT We have developed a hybrid code GMEC: Gyro-kinetic Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Energetic-particle Code that can numerically simulate energetic particle-driven Alfvén eigenmodes and energetic particle transport in tokamak plasmas. In order to resolve the Alfvén eigenmodes with high toroidal numbers effectively, the field-aligned coordinates and meshes are adopted. The extended MHD equations are solved with the five-point finite difference method and the fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. The gyrokinetic equations are solved by particle-in-cell method for the perturbed energetic particle pressures that are coupled into the MHD equations. Up to now, a simplified version of the hybrid code has been completed with several successful verifications, including linear simulations of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes and reversed shear Alfvén eigenmodes.
-
 On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas Liu Chen1,2,3, Zhiyong Qiu1,3,∗ and Fulvio Zonca1,31 Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, School of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China 2 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697-4575, United States of America 3 Center for Nonlinear Plasma Science and C.R. ENEA Frascati, C.P. 65, 00044 Frascati, Italy E-mail: zqiu@zju.edu.cn Received 19 March 2023, revised 1 August 2023 Accepted for publication 21 August 2023 Published 7 September 2023Abstract:Using electron drift wave (eDW) as a paradigm model, we have investigated analytically direct wave–wave interactions between a test DW and ambient toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes (TAEs) in toroidal plasmas, and their effects on the stability of the eDW. The nonlinear effects enter via scatterings to short-wavelength electron Landau damped kinetic Alfvén waves (KAWs). Specifically, it is found that scatterings to upper-sideband KAW lead to stimulated absorption of eDW. Scatterings to the lower-sideband KAW, on the contrary, lead to its spontaneous emission. As a consequence, for typical parameters and fluctuation intensity, nonlinear scatterings by TAEs have negligible net effects on the eDW stability; in contrast to the ‘reverse’ process investigated in Chen et al (2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 094001), where it is shown that nonlinear scattering by ambient eDWs may lead to significant damping of TAE.Keywords: toroidal Alfvén eigenmode, burning plasma, drift wave, nonlinear mode coupling, gyrokinetic theory (Some figures may appear in colour only in the online journal)
On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas Liu Chen1,2,3, Zhiyong Qiu1,3,∗ and Fulvio Zonca1,31 Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, School of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China 2 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697-4575, United States of America 3 Center for Nonlinear Plasma Science and C.R. ENEA Frascati, C.P. 65, 00044 Frascati, Italy E-mail: zqiu@zju.edu.cn Received 19 March 2023, revised 1 August 2023 Accepted for publication 21 August 2023 Published 7 September 2023Abstract:Using electron drift wave (eDW) as a paradigm model, we have investigated analytically direct wave–wave interactions between a test DW and ambient toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes (TAEs) in toroidal plasmas, and their effects on the stability of the eDW. The nonlinear effects enter via scatterings to short-wavelength electron Landau damped kinetic Alfvén waves (KAWs). Specifically, it is found that scatterings to upper-sideband KAW lead to stimulated absorption of eDW. Scatterings to the lower-sideband KAW, on the contrary, lead to its spontaneous emission. As a consequence, for typical parameters and fluctuation intensity, nonlinear scatterings by TAEs have negligible net effects on the eDW stability; in contrast to the ‘reverse’ process investigated in Chen et al (2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 094001), where it is shown that nonlinear scattering by ambient eDWs may lead to significant damping of TAE.Keywords: toroidal Alfvén eigenmode, burning plasma, drift wave, nonlinear mode coupling, gyrokinetic theory (Some figures may appear in colour only in the online journal)
-
 巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制
2024-10-14
聚变理论与模拟中心
北宋时期的司天监于1054年记录了一次超新星爆发,这一事件形成了一颗半径约10公里的中子星和包裹它的蟹状星云。巧合的是,该中子星的磁轴恰好对准了6500光年外的地球。通过高速自转,中子星沿着磁轴发出的电磁辐射每秒扫过地球30次。1968年,科学家首次探测到来自这颗中子星的巨脉冲(giant pulse)无线电波。2003年,Hankins的观测结果显示这些巨脉冲由众多仅1纳秒宽的子脉冲堆积而成,并且这些子脉冲具有极高的圆偏振度。左图:蟹状星云;右图:中子星辐射示意图2007年,Lorimer首次报道了快射电暴(fast radio burst),可以说快射电暴是近年来天文领域最重要的意外发现。2020年,人们观测到银河系内一颗磁星(磁场更强的中子星)爆发了快射电暴。与巨脉冲相似,部分快射电暴也展现出高度的圆偏振。然而,巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制至今尚不明确。等间隔双线分布的巨脉冲信号本研究首次在蟹状星云中子星的一个巨脉冲中发现了等间隔成对分布的子脉冲。每对脉冲中,第一个为左旋圆偏振,第二个为右旋圆偏振。上图展示了9对子脉冲的配对情况,成对子脉冲的时间间隔均在21微秒左右,不确定度仅为0.8微秒。理论上,法拉第效应可以用于解释这一现象。然而,中子星磁层内的等离子体由电子和正电子组成,沿磁场方向观测,它们的回旋运动对左右圆偏振是对称的,因此法拉第效应不起作用。我们大胆假设中子星磁层内的正负电子等离子体存在高度不对称性,即正负电荷没有完全中和,或正负电子能量存在显著差异。在这种不对称等离子体中,法拉第效应会将一个线偏振波分裂成前后延迟的左右圆偏振模式。在磁层参数允许的范围内,只有考虑巨脉冲的相对论强场效应,我们才能计算出符合观测结果的一对圆偏振射电脉冲。该理论还成功解释了巨脉冲的反常色散和随机偏振角等特异现象。此外,已有观测表明某些快射电暴也包含纳秒量级的子脉冲,其圆偏振可以用类似的机制进行解释。鉴于广泛认为中子星磁场方向上存在电场,这些电场可以加速正负电子,并可能诱发所假设的等离子体不对称性。此外,部分磁层粒子模拟结果也显示出不对称等离子体的迹象。关于巨脉冲和快射电暴的产生机制,学术界尚无定论,根本原因在于我们对中子星磁层的认识不足。通过观察中子星的电磁辐射,难以推断出更多有用的磁层信息。本研究发现的纳秒级成对巨脉冲可作为一种诊断磁层的新工具,有望帮助确定中子星磁层的等离子体参数。该研究由浙江大学物理学院武慧春教授完成,近日发表在《Astrophysical Journal Letters》。论文链接:https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/ad8154
巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制
2024-10-14
聚变理论与模拟中心
北宋时期的司天监于1054年记录了一次超新星爆发,这一事件形成了一颗半径约10公里的中子星和包裹它的蟹状星云。巧合的是,该中子星的磁轴恰好对准了6500光年外的地球。通过高速自转,中子星沿着磁轴发出的电磁辐射每秒扫过地球30次。1968年,科学家首次探测到来自这颗中子星的巨脉冲(giant pulse)无线电波。2003年,Hankins的观测结果显示这些巨脉冲由众多仅1纳秒宽的子脉冲堆积而成,并且这些子脉冲具有极高的圆偏振度。左图:蟹状星云;右图:中子星辐射示意图2007年,Lorimer首次报道了快射电暴(fast radio burst),可以说快射电暴是近年来天文领域最重要的意外发现。2020年,人们观测到银河系内一颗磁星(磁场更强的中子星)爆发了快射电暴。与巨脉冲相似,部分快射电暴也展现出高度的圆偏振。然而,巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制至今尚不明确。等间隔双线分布的巨脉冲信号本研究首次在蟹状星云中子星的一个巨脉冲中发现了等间隔成对分布的子脉冲。每对脉冲中,第一个为左旋圆偏振,第二个为右旋圆偏振。上图展示了9对子脉冲的配对情况,成对子脉冲的时间间隔均在21微秒左右,不确定度仅为0.8微秒。理论上,法拉第效应可以用于解释这一现象。然而,中子星磁层内的等离子体由电子和正电子组成,沿磁场方向观测,它们的回旋运动对左右圆偏振是对称的,因此法拉第效应不起作用。我们大胆假设中子星磁层内的正负电子等离子体存在高度不对称性,即正负电荷没有完全中和,或正负电子能量存在显著差异。在这种不对称等离子体中,法拉第效应会将一个线偏振波分裂成前后延迟的左右圆偏振模式。在磁层参数允许的范围内,只有考虑巨脉冲的相对论强场效应,我们才能计算出符合观测结果的一对圆偏振射电脉冲。该理论还成功解释了巨脉冲的反常色散和随机偏振角等特异现象。此外,已有观测表明某些快射电暴也包含纳秒量级的子脉冲,其圆偏振可以用类似的机制进行解释。鉴于广泛认为中子星磁场方向上存在电场,这些电场可以加速正负电子,并可能诱发所假设的等离子体不对称性。此外,部分磁层粒子模拟结果也显示出不对称等离子体的迹象。关于巨脉冲和快射电暴的产生机制,学术界尚无定论,根本原因在于我们对中子星磁层的认识不足。通过观察中子星的电磁辐射,难以推断出更多有用的磁层信息。本研究发现的纳秒级成对巨脉冲可作为一种诊断磁层的新工具,有望帮助确定中子星磁层的等离子体参数。该研究由浙江大学物理学院武慧春教授完成,近日发表在《Astrophysical Journal Letters》。论文链接:https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/ad8154
-
 Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
45.Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas.pdf
Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
45.Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas.pdf
-
 Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
44.Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection.pdf
Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
44.Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection.pdf
-
 Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
43.Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles.pdf
Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
43.Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles.pdf
-
 On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
42.On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas.pdf
On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
42.On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas.pdf
-
 Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
41.Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode.pdf
Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
41.Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode.pdf
-
 Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
40.Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak.pdf
Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
40.Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak.pdf
-
 Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
39.Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak.pdf
Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
39.Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak.pdf
-
 Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
38.Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode.pdf
Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
38.Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode.pdf
-
 Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
37.Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak.pdf
Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
37.Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak.pdf
-
 On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
36.On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function.pdf
On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
36.On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function.pdf
 An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations J. Wang a , J.M. Duan b , Z.W. Ma a,* , W. Zhang a a:Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, Chinab:Ecole ´ Polytechnique F´ed´erale de Lausanne, 1015 Lausanne, SwitzerlandAn adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme is developed for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) simulations, based on the CLT code (S. Wang and Z.W. Ma, Phys. Plasmas, 2015). Our numerical scheme is built on the MHD equations in curvilinear coordinates, based on a coordinate transformation from the physical domain to a computational domain. The scheme is constructed on a uniform Cartesian computational mesh that is obtained from a non-uniform adaptive moving mesh in the physical domain through the coordinate transformation. Mesh points in the physical domain in general move and concentrate in the vicinity of solutions with rapid variations by solving an adaptive mesh equation, whilst total number of mesh points remains unchanged. The local resolution can be significantly increased and computational resource is largely reduced. Comparison between results obtained with the original uniform mesh and the new adaptive moving mesh is carried out by simulation of the linear and nonlinear 2/1 tearing mode, linear and nonlinear 1/1 resistive internal kink mode. It is found that the adaptive moving mesh scheme possesses better numerical stability and convergence.
An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
An adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic simulations J. Wang a , J.M. Duan b , Z.W. Ma a,* , W. Zhang a a:Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, Chinab:Ecole ´ Polytechnique F´ed´erale de Lausanne, 1015 Lausanne, SwitzerlandAn adaptive moving mesh finite difference scheme is developed for tokamak magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) simulations, based on the CLT code (S. Wang and Z.W. Ma, Phys. Plasmas, 2015). Our numerical scheme is built on the MHD equations in curvilinear coordinates, based on a coordinate transformation from the physical domain to a computational domain. The scheme is constructed on a uniform Cartesian computational mesh that is obtained from a non-uniform adaptive moving mesh in the physical domain through the coordinate transformation. Mesh points in the physical domain in general move and concentrate in the vicinity of solutions with rapid variations by solving an adaptive mesh equation, whilst total number of mesh points remains unchanged. The local resolution can be significantly increased and computational resource is largely reduced. Comparison between results obtained with the original uniform mesh and the new adaptive moving mesh is carried out by simulation of the linear and nonlinear 2/1 tearing mode, linear and nonlinear 1/1 resistive internal kink mode. It is found that the adaptive moving mesh scheme possesses better numerical stability and convergence.
 Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfven eigenmodes driven by energetic particles
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfvén eigenmodes driven by energetic particles Z. Y. Liu ; P. Y. Jiang ; S. Y. Liu ; L. L. Zhang ; G. Y. Fu ABSTRACT We have developed a hybrid code GMEC: Gyro-kinetic Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Energetic-particle Code that can numerically simulate energetic particle-driven Alfvén eigenmodes and energetic particle transport in tokamak plasmas. In order to resolve the Alfvén eigenmodes with high toroidal numbers effectively, the field-aligned coordinates and meshes are adopted. The extended MHD equations are solved with the five-point finite difference method and the fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. The gyrokinetic equations are solved by particle-in-cell method for the perturbed energetic particle pressures that are coupled into the MHD equations. Up to now, a simplified version of the hybrid code has been completed with several successful verifications, including linear simulations of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes and reversed shear Alfvén eigenmodes.
Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfven eigenmodes driven by energetic particles
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
Development of a gyrokinetic-MHD energetic particle simulation code. II. Linear simulations of Alfvén eigenmodes driven by energetic particles Z. Y. Liu ; P. Y. Jiang ; S. Y. Liu ; L. L. Zhang ; G. Y. Fu ABSTRACT We have developed a hybrid code GMEC: Gyro-kinetic Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Energetic-particle Code that can numerically simulate energetic particle-driven Alfvén eigenmodes and energetic particle transport in tokamak plasmas. In order to resolve the Alfvén eigenmodes with high toroidal numbers effectively, the field-aligned coordinates and meshes are adopted. The extended MHD equations are solved with the five-point finite difference method and the fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. The gyrokinetic equations are solved by particle-in-cell method for the perturbed energetic particle pressures that are coupled into the MHD equations. Up to now, a simplified version of the hybrid code has been completed with several successful verifications, including linear simulations of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes and reversed shear Alfvén eigenmodes.
 On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas Liu Chen1,2,3, Zhiyong Qiu1,3,∗ and Fulvio Zonca1,31 Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, School of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China 2 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697-4575, United States of America 3 Center for Nonlinear Plasma Science and C.R. ENEA Frascati, C.P. 65, 00044 Frascati, Italy E-mail: zqiu@zju.edu.cn Received 19 March 2023, revised 1 August 2023 Accepted for publication 21 August 2023 Published 7 September 2023Abstract:Using electron drift wave (eDW) as a paradigm model, we have investigated analytically direct wave–wave interactions between a test DW and ambient toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes (TAEs) in toroidal plasmas, and their effects on the stability of the eDW. The nonlinear effects enter via scatterings to short-wavelength electron Landau damped kinetic Alfvén waves (KAWs). Specifically, it is found that scatterings to upper-sideband KAW lead to stimulated absorption of eDW. Scatterings to the lower-sideband KAW, on the contrary, lead to its spontaneous emission. As a consequence, for typical parameters and fluctuation intensity, nonlinear scatterings by TAEs have negligible net effects on the eDW stability; in contrast to the ‘reverse’ process investigated in Chen et al (2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 094001), where it is shown that nonlinear scattering by ambient eDWs may lead to significant damping of TAE.Keywords: toroidal Alfvén eigenmode, burning plasma, drift wave, nonlinear mode coupling, gyrokinetic theory (Some figures may appear in colour only in the online journal)
On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas
2024-11-08
聚变理论与模拟中心
On nonlinear scattering of drift wave by toroidal Alfvén eigenmode in tokamak plasmas Liu Chen1,2,3, Zhiyong Qiu1,3,∗ and Fulvio Zonca1,31 Institute for Fusion Theory and Simulation, School of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China 2 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697-4575, United States of America 3 Center for Nonlinear Plasma Science and C.R. ENEA Frascati, C.P. 65, 00044 Frascati, Italy E-mail: zqiu@zju.edu.cn Received 19 March 2023, revised 1 August 2023 Accepted for publication 21 August 2023 Published 7 September 2023Abstract:Using electron drift wave (eDW) as a paradigm model, we have investigated analytically direct wave–wave interactions between a test DW and ambient toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes (TAEs) in toroidal plasmas, and their effects on the stability of the eDW. The nonlinear effects enter via scatterings to short-wavelength electron Landau damped kinetic Alfvén waves (KAWs). Specifically, it is found that scatterings to upper-sideband KAW lead to stimulated absorption of eDW. Scatterings to the lower-sideband KAW, on the contrary, lead to its spontaneous emission. As a consequence, for typical parameters and fluctuation intensity, nonlinear scatterings by TAEs have negligible net effects on the eDW stability; in contrast to the ‘reverse’ process investigated in Chen et al (2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 094001), where it is shown that nonlinear scattering by ambient eDWs may lead to significant damping of TAE.Keywords: toroidal Alfvén eigenmode, burning plasma, drift wave, nonlinear mode coupling, gyrokinetic theory (Some figures may appear in colour only in the online journal)
 巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制
2024-10-14
聚变理论与模拟中心
北宋时期的司天监于1054年记录了一次超新星爆发,这一事件形成了一颗半径约10公里的中子星和包裹它的蟹状星云。巧合的是,该中子星的磁轴恰好对准了6500光年外的地球。通过高速自转,中子星沿着磁轴发出的电磁辐射每秒扫过地球30次。1968年,科学家首次探测到来自这颗中子星的巨脉冲(giant pulse)无线电波。2003年,Hankins的观测结果显示这些巨脉冲由众多仅1纳秒宽的子脉冲堆积而成,并且这些子脉冲具有极高的圆偏振度。左图:蟹状星云;右图:中子星辐射示意图2007年,Lorimer首次报道了快射电暴(fast radio burst),可以说快射电暴是近年来天文领域最重要的意外发现。2020年,人们观测到银河系内一颗磁星(磁场更强的中子星)爆发了快射电暴。与巨脉冲相似,部分快射电暴也展现出高度的圆偏振。然而,巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制至今尚不明确。等间隔双线分布的巨脉冲信号本研究首次在蟹状星云中子星的一个巨脉冲中发现了等间隔成对分布的子脉冲。每对脉冲中,第一个为左旋圆偏振,第二个为右旋圆偏振。上图展示了9对子脉冲的配对情况,成对子脉冲的时间间隔均在21微秒左右,不确定度仅为0.8微秒。理论上,法拉第效应可以用于解释这一现象。然而,中子星磁层内的等离子体由电子和正电子组成,沿磁场方向观测,它们的回旋运动对左右圆偏振是对称的,因此法拉第效应不起作用。我们大胆假设中子星磁层内的正负电子等离子体存在高度不对称性,即正负电荷没有完全中和,或正负电子能量存在显著差异。在这种不对称等离子体中,法拉第效应会将一个线偏振波分裂成前后延迟的左右圆偏振模式。在磁层参数允许的范围内,只有考虑巨脉冲的相对论强场效应,我们才能计算出符合观测结果的一对圆偏振射电脉冲。该理论还成功解释了巨脉冲的反常色散和随机偏振角等特异现象。此外,已有观测表明某些快射电暴也包含纳秒量级的子脉冲,其圆偏振可以用类似的机制进行解释。鉴于广泛认为中子星磁场方向上存在电场,这些电场可以加速正负电子,并可能诱发所假设的等离子体不对称性。此外,部分磁层粒子模拟结果也显示出不对称等离子体的迹象。关于巨脉冲和快射电暴的产生机制,学术界尚无定论,根本原因在于我们对中子星磁层的认识不足。通过观察中子星的电磁辐射,难以推断出更多有用的磁层信息。本研究发现的纳秒级成对巨脉冲可作为一种诊断磁层的新工具,有望帮助确定中子星磁层的等离子体参数。该研究由浙江大学物理学院武慧春教授完成,近日发表在《Astrophysical Journal Letters》。论文链接:https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/ad8154
巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制
2024-10-14
聚变理论与模拟中心
北宋时期的司天监于1054年记录了一次超新星爆发,这一事件形成了一颗半径约10公里的中子星和包裹它的蟹状星云。巧合的是,该中子星的磁轴恰好对准了6500光年外的地球。通过高速自转,中子星沿着磁轴发出的电磁辐射每秒扫过地球30次。1968年,科学家首次探测到来自这颗中子星的巨脉冲(giant pulse)无线电波。2003年,Hankins的观测结果显示这些巨脉冲由众多仅1纳秒宽的子脉冲堆积而成,并且这些子脉冲具有极高的圆偏振度。左图:蟹状星云;右图:中子星辐射示意图2007年,Lorimer首次报道了快射电暴(fast radio burst),可以说快射电暴是近年来天文领域最重要的意外发现。2020年,人们观测到银河系内一颗磁星(磁场更强的中子星)爆发了快射电暴。与巨脉冲相似,部分快射电暴也展现出高度的圆偏振。然而,巨脉冲和快射电暴的圆偏振机制至今尚不明确。等间隔双线分布的巨脉冲信号本研究首次在蟹状星云中子星的一个巨脉冲中发现了等间隔成对分布的子脉冲。每对脉冲中,第一个为左旋圆偏振,第二个为右旋圆偏振。上图展示了9对子脉冲的配对情况,成对子脉冲的时间间隔均在21微秒左右,不确定度仅为0.8微秒。理论上,法拉第效应可以用于解释这一现象。然而,中子星磁层内的等离子体由电子和正电子组成,沿磁场方向观测,它们的回旋运动对左右圆偏振是对称的,因此法拉第效应不起作用。我们大胆假设中子星磁层内的正负电子等离子体存在高度不对称性,即正负电荷没有完全中和,或正负电子能量存在显著差异。在这种不对称等离子体中,法拉第效应会将一个线偏振波分裂成前后延迟的左右圆偏振模式。在磁层参数允许的范围内,只有考虑巨脉冲的相对论强场效应,我们才能计算出符合观测结果的一对圆偏振射电脉冲。该理论还成功解释了巨脉冲的反常色散和随机偏振角等特异现象。此外,已有观测表明某些快射电暴也包含纳秒量级的子脉冲,其圆偏振可以用类似的机制进行解释。鉴于广泛认为中子星磁场方向上存在电场,这些电场可以加速正负电子,并可能诱发所假设的等离子体不对称性。此外,部分磁层粒子模拟结果也显示出不对称等离子体的迹象。关于巨脉冲和快射电暴的产生机制,学术界尚无定论,根本原因在于我们对中子星磁层的认识不足。通过观察中子星的电磁辐射,难以推断出更多有用的磁层信息。本研究发现的纳秒级成对巨脉冲可作为一种诊断磁层的新工具,有望帮助确定中子星磁层的等离子体参数。该研究由浙江大学物理学院武慧春教授完成,近日发表在《Astrophysical Journal Letters》。论文链接:https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/ad8154
 Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
45.Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas.pdf
Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
45.Effects of Radial Envelope Modulations on the Collisionless Trapped-electron Mode in Tokamak Plasmas.pdf
 Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
44.Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection.pdf
Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
44.Effective Resistivity in Collisionless Magnetic Reconnection.pdf
 Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
43.Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles.pdf
Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
43.Short Wavelength Geodesic Acoustic Mode Excitation by Energetic Particles.pdf
 On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
42.On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas.pdf
On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
42.On Drift Wave Instabilities Excited by Strong Plasma Gradients in Toroidal Plasmas.pdf
 Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
41.Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode.pdf
Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
41.Nonlinear simulation of toroidal Alfvén eigenmodes in the presence of a tearing mode.pdf
 Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
40.Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak.pdf
Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
40.Effect of electron-to-ion mass ratio on radial electric field generation in tokamak.pdf
 Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
39.Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak.pdf
Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
39.Hall Effect on Tearing Mode Instabilities in Tokamak.pdf
 Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
38.Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode.pdf
Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
38.Radial properties of the geodesic acoustic mode.pdf
 Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
37.Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak.pdf
Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
37.Numerical Study on Wave-induced Beam Ion Prompt Losses in DIII-D Tokamak.pdf
 On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
36.On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function.pdf
On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function
2018-07-30
聚变理论与模拟中心英文网
36.On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function.pdf